Derrière la multitude des morts les pesticides se dissimulent comme des coupables.
Behind Mass Die-offs Pesticides Lurk as Culprit
Sonia SHAH, Environnement 360, 07 JAN 2010 : Report
http://e360.yale.edu/content/feature.msp?id=2228
Derrière la multitude des morts les pesticides se dissimulent comme des coupables
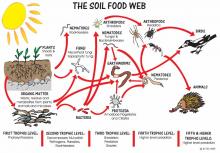
Durant les douze dernières années, trois nouvelles maladies ont décimé les populations d’amphibiens, d’abeilles, et, plus récemment, de chauve-souris.
De plus en plus, des scientifiques suspectent que l’exposition aux faibles doses de pesticides pourrait contribuer à cette éruption d’épidémies.