The Urgent Need for a New Concept in Agriculture
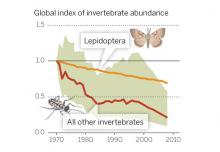
The industrialization of the agricultural sector has increased the chemical burden on natural ecosystems. Pesticides are agrochemicals used in agricultural lands, public health programs, and urban green areas in order to protect plants and humans from various diseases. However, due to their known ability to cause a large number of negative health and environmental effects, their side effects can be an important environmental health risk factor.