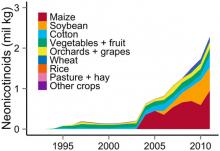
Seasonal hawk count over Greenwich shows declines
Researchers at Audubon Greenwich’s Quaker Ridge hawk watch site are alarmed that they’ve seen only 8,025 hawks over the fall migration season this year, the second lowest total in more than three decades of collecting data. In years past, they have seen as many as 30,000 hawks in a single day, said Ryan MacLean, the official hawk counter at the site. “We have 31 years of data, and unfortunately out of 31 years, this is our second lowest on record,” MacLean said.