De pesticiden lobby ondermijnt met steun van EU lidstaten effectieve bescherming van bijen en andere insecten
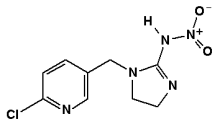
Begin april liet FTM zien dat Nederland invoering van de Bee Guidance, een Europees richtsnoer om bijen te beschermen, al jarenlang tegenwerkt. Die onthulling leidde tot een Kamerdebat, waarin minister Schouten (Landbouw) de Kamer gedetailleerde inzage in het dossier beloofde. Uit de stukken die zo openbaar zijn geworden, blijkt opnieuw iets opmerkelijks: Nederland heeft bij de Europese Commissie gepleit voor een nieuw rekenmodel om bijenpopulaties te monitoren. En dat model wordt gepusht door de chemische industrie.