Neonicotinoids: Systemic Insecticides and Systematic Failure
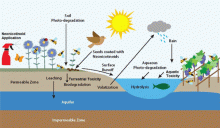
The widespread adoption and use of neonicotinoid compounds originally considered to be environmentally benign can now potentially be considered to be an environmental catastrophe. While the generational development and production of neonicotinoids has focused on making these insecticides more potent to their target organisms at very small dosages, their adverse environmental consequences have largely remained overlooked. Imidacloprid was the first generation neonicotinoid to receive widespread attention for its environmental consequences.