Effects of acetamiprid and thiacloprid in their commercial formulations on soil fauna
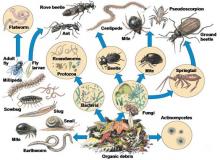
Neonicotinoids are the most prominent group of insecticides in the world and are commercialized in over 120 countries for the control of agricultural pests mainly due to their broad-spectrum activity and versatility in application. Though non-target soil organisms are likely to be exposed during application, there is paucity of information in scientific literature regarding their sensitivity to neonicotinoids.